画像 plot x 2(y-^×)2=1 325483
Draw The Graph Of Y X 2 X And Hence Solve X 2 1 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
1 Suppose the joint pmf of X and Y isgiven byp(1,1) = 05, p(1,2) = 01, p(2,1) = 01, p(2,2) = 03 Find the pmf of X given Y = 1 Solution pXY=1(1) = p(1,1)/pY (1) = 05/06 = 5/6 pXY=1(2) = p(2,1)/pY (1) = 01/06 = 1/6 2 If X and Y are independent Poisson RVs with respective means λ1 and λ2, find the conditional pmf of X3dprinting, solidworks f(0,0,0) is 0, not 1 (the isosurface level), so you only get points drawn completing the cones if there are enough points near the origin that happen to have value 1 But when you switch to linspace(,,), the closest coordinates to the origin are at about 105, leaving a gap of about 21
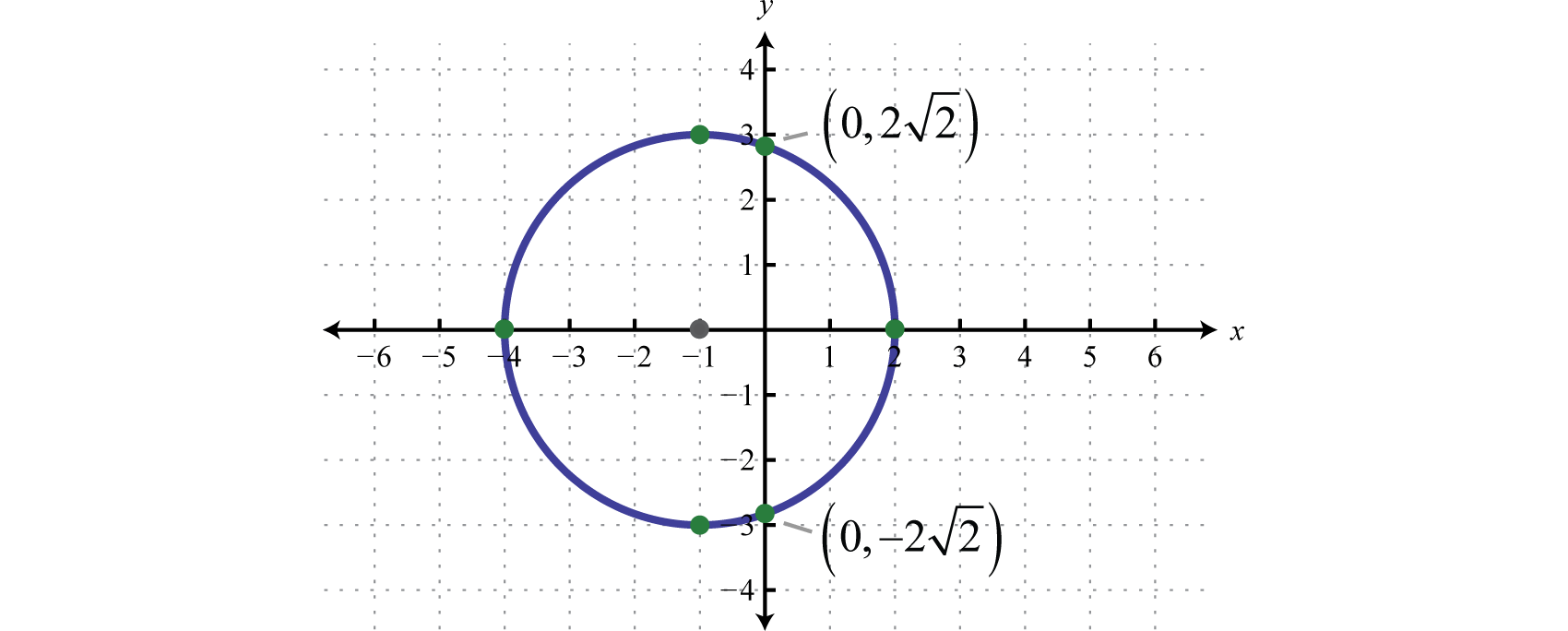
Plot x 2(y-^×)2=1
Plot x 2(y-^×)2=1-3D Surface Plotter An online tool to create 3D plots of surfaces This demo allows you to enter a mathematical expression in terms of x and y When you hit the calculate button, the demo will calculate the value of the expression over the x and y ranges provided and then plot the result as a surface The graph can be zoomed in by scrolling Explanation This is the equation of a circle with its centre at the origin Think of the axis as the sides of a triangle with the Hypotenuse being the line from the centre to the point on the circle By using Pythagoras you would end up with the equation given where the 4 is in fact r2 To obtain the plot points manipulate the equation as below Given x2 y2 = r2 → x2 y2 = 4
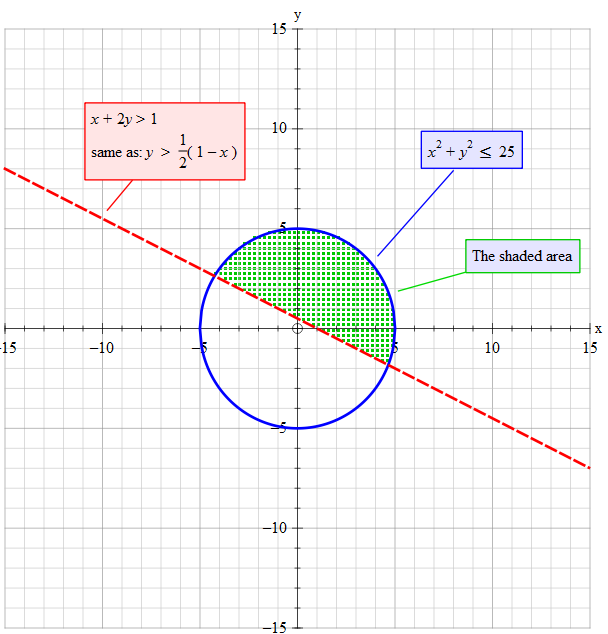
How Do You Solve The System X 2y 1 And X 2 Y 2 25 By Graphing Socratic
Plot X^2(y2)^21 Natural Language; Chapter 4 Visualization with Matplotlib We'll now take an indepth look at the Matplotlib tool for visualization in Python Matplotlib is a multiplatform data visualization library built on NumPy arrays, Selection from Python Data Science Handbook BookIntegrals in cylindrical, spherical coordinates (Sect 157) I Integration in spherical coordinates I Review Cylindrical coordinates I Spherical coordinates in space I Triple integral in spherical coordinates Spherical coordinates in R3 Definition The spherical coordinates of a point P ∈ R3 is the ordered triple (ρ,φ,θ) defined by the picture
Plot y=x^2 Natural Language;Plot (x, y, 'b', 'LineWidth', 2); 3Dplot of "x^2y^2z^2=1" Learn more about isosurface;
Plot x 2(y-^×)2=1のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | 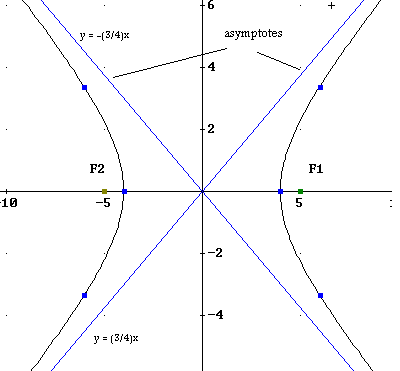 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | 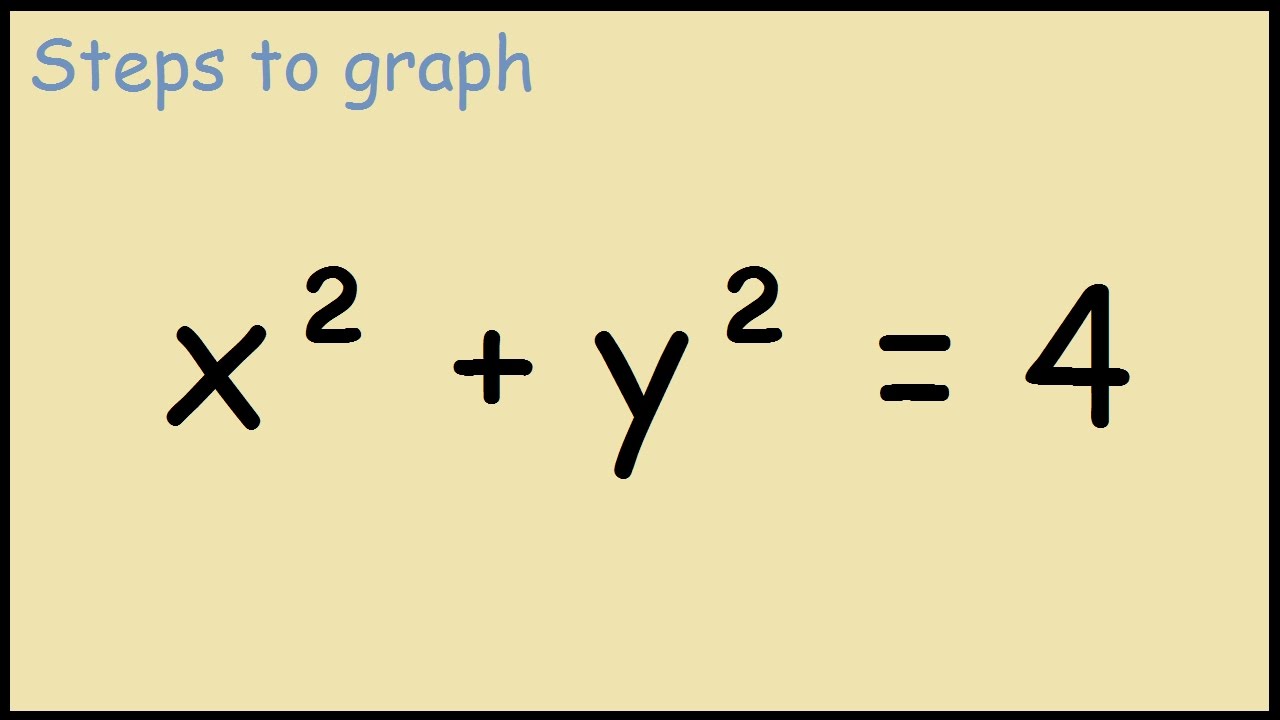 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas | 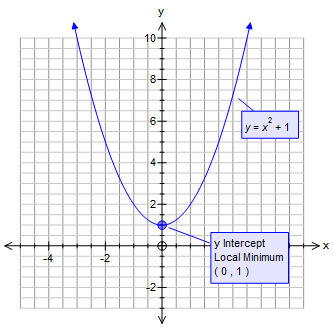 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
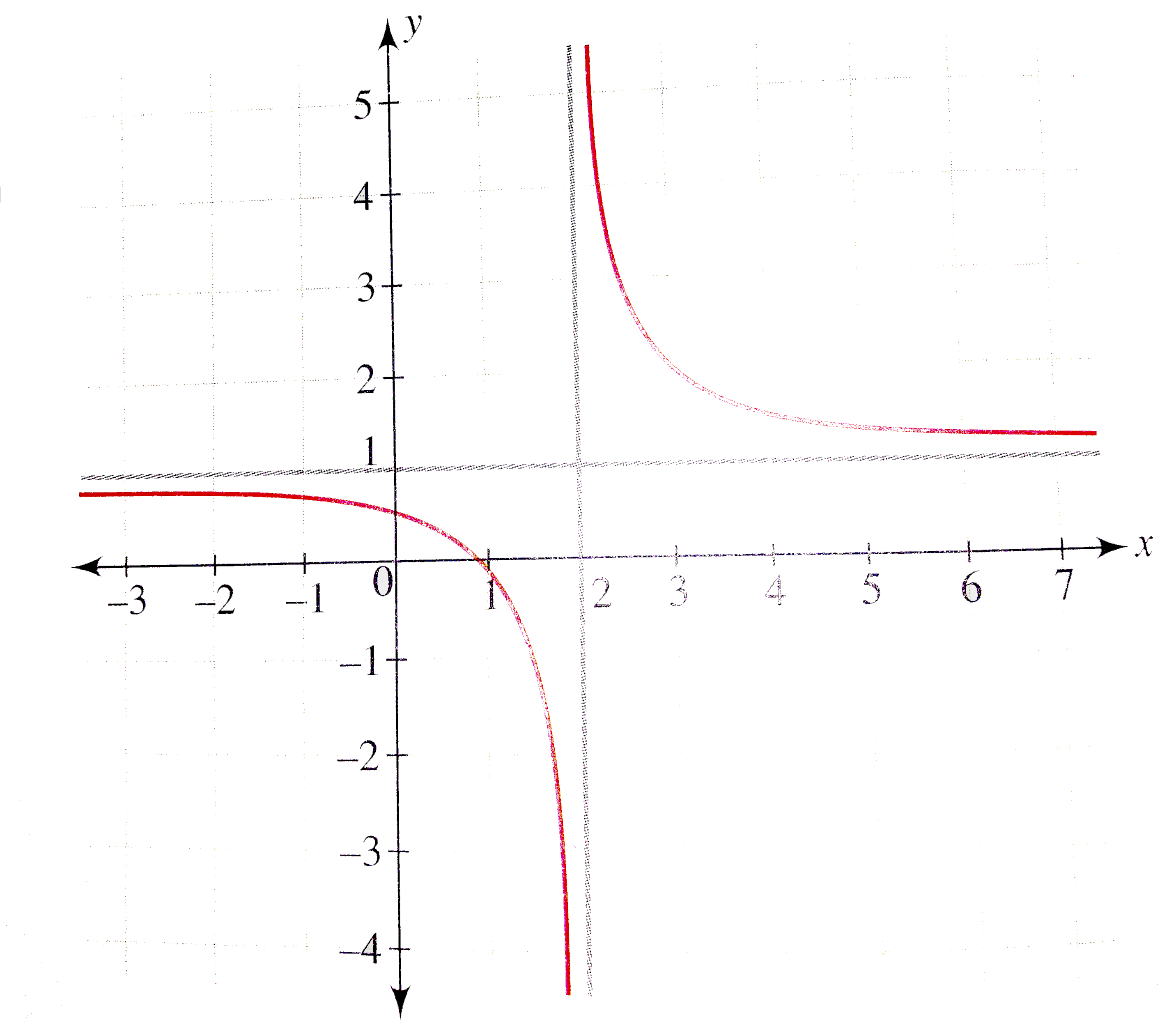 Graphing Parabolas | 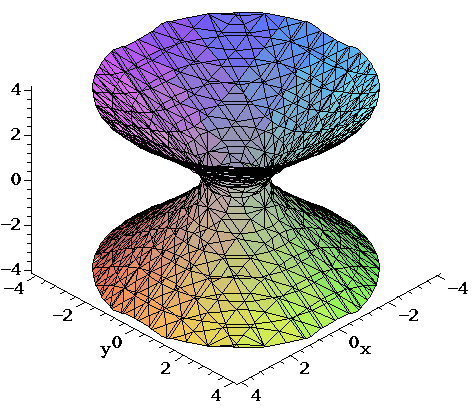 Graphing Parabolas | 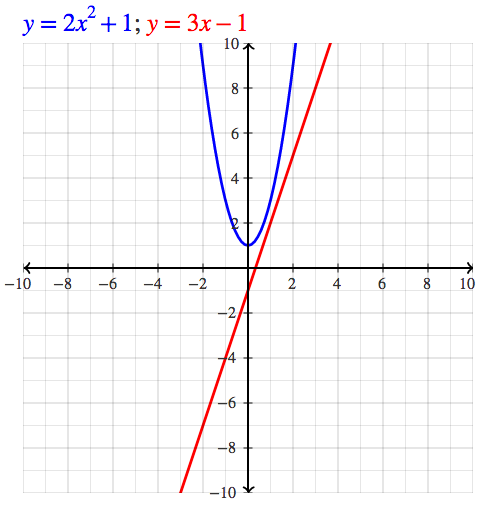 Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
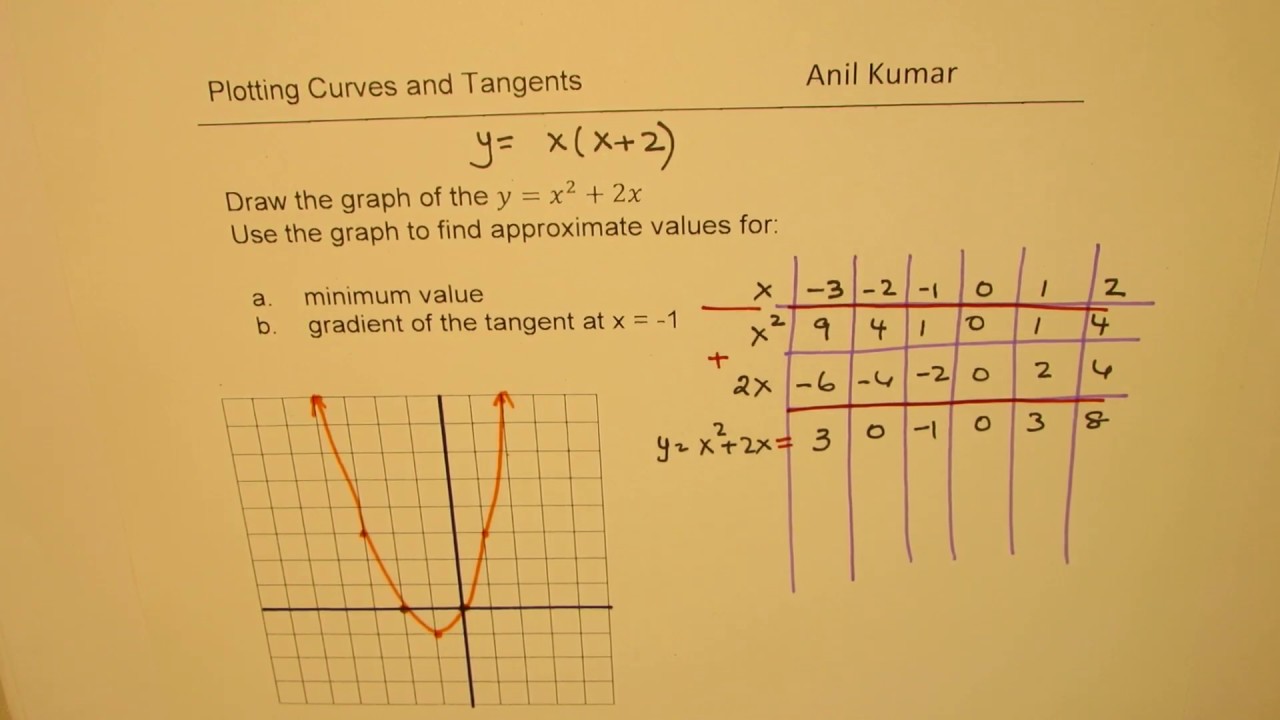 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | 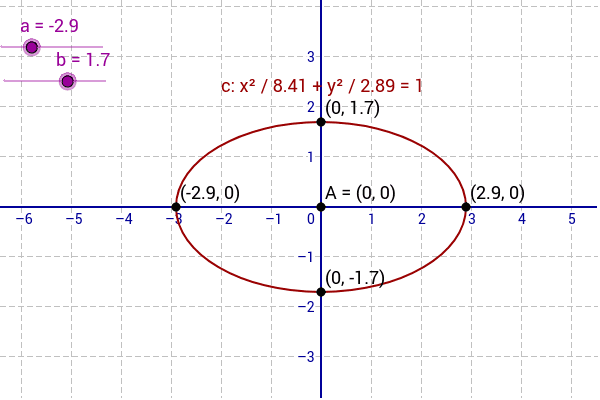 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas | 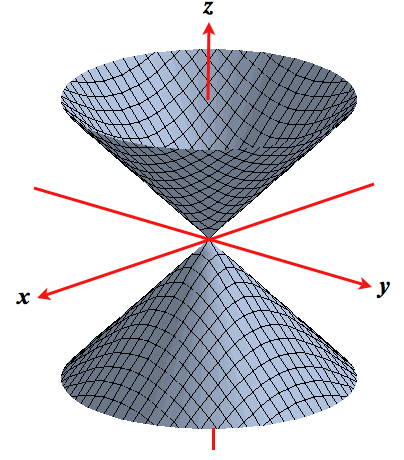 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | 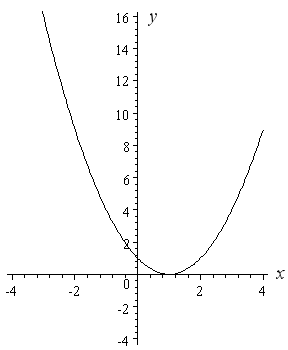 Graphing Parabolas | 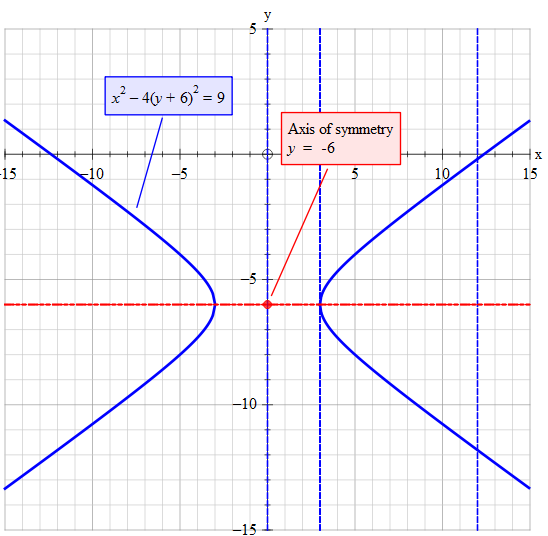 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | 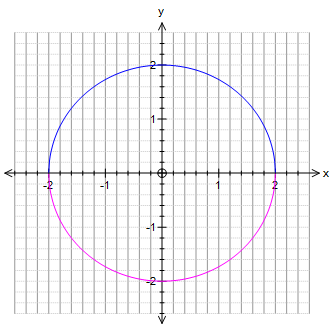 Graphing Parabolas | 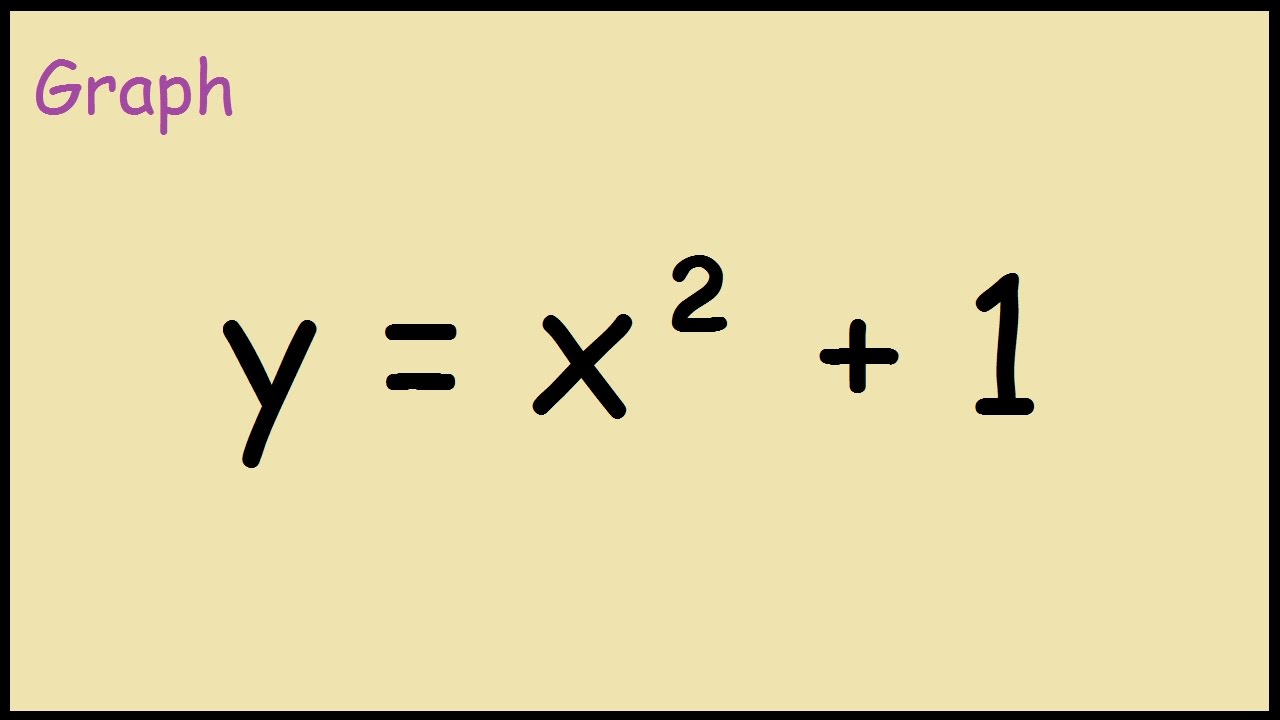 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | 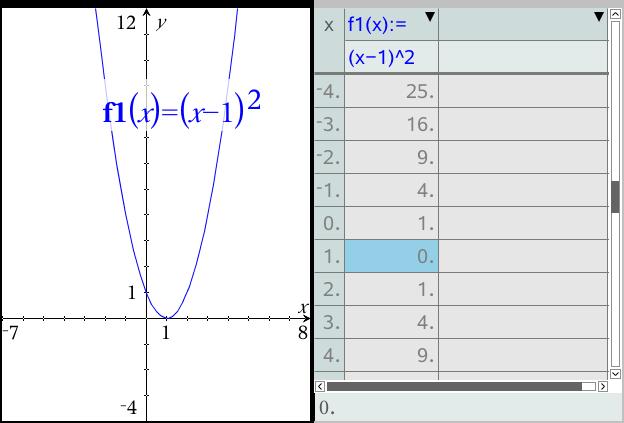 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
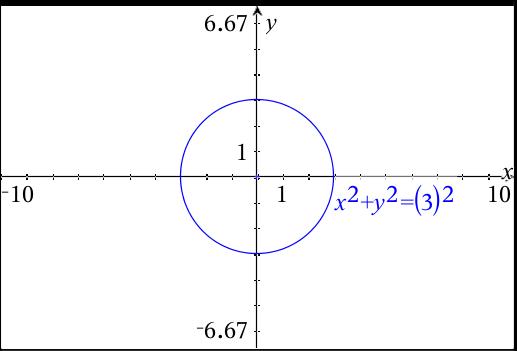 Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
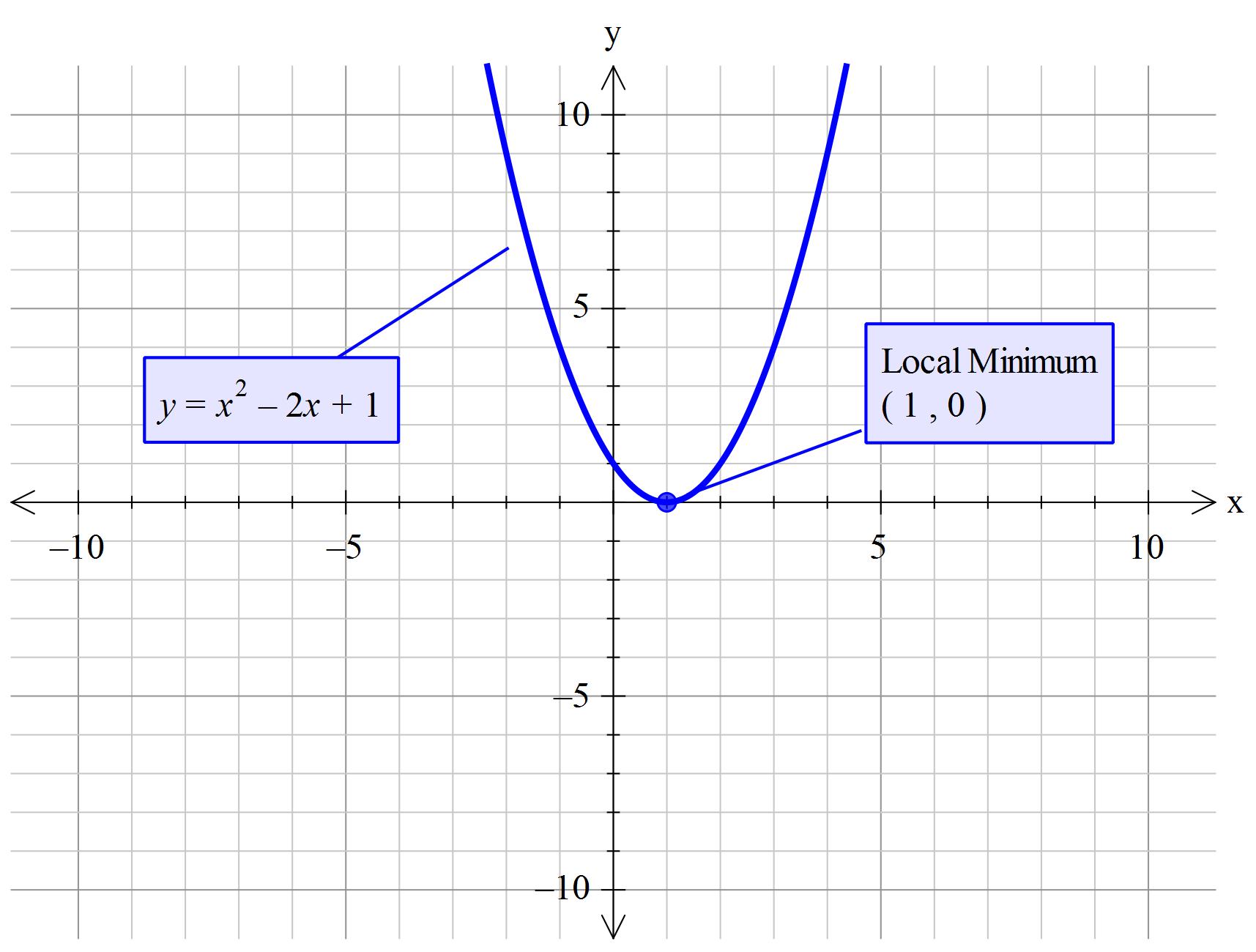 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | 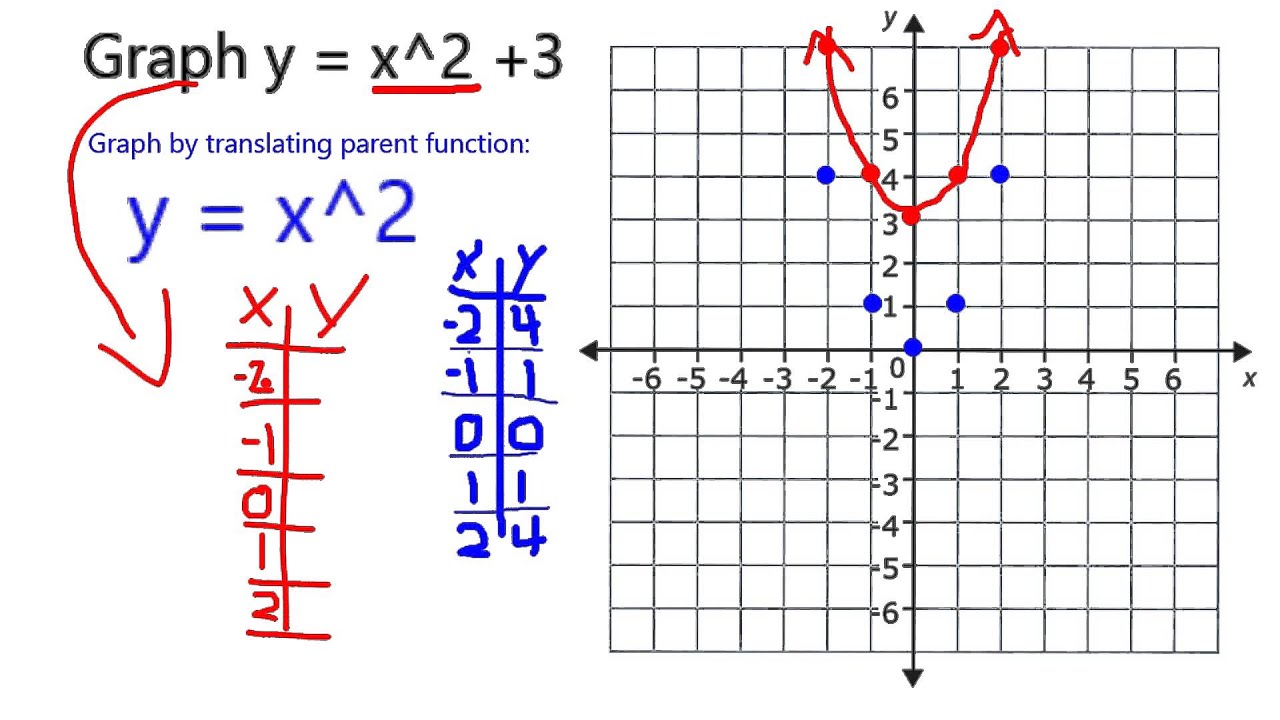 Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas | Graphing Parabolas |
Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |  Graphing Parabolas |
 Graphing Parabolas | 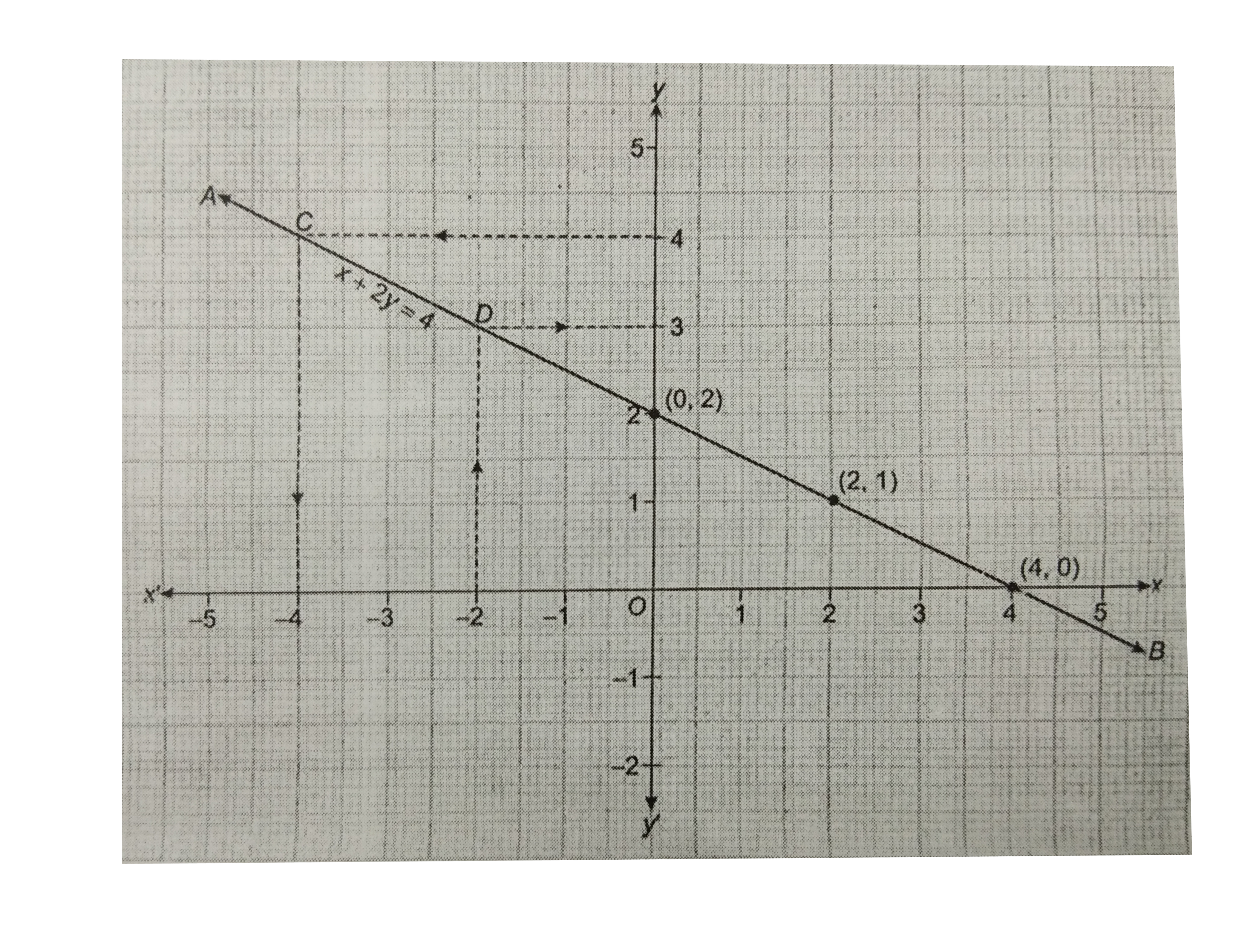 Graphing Parabolas |
\(x_1 \mathit{v1} x_2 \mathit{v2} = v3\) or \(x_1 x_2v1;Ch 27 Numerical Approximations Euler's Method • Recall that a first order initial value problem has the form • If f and f / y are continuous, then this IVP has a unique solution y = (t) in some interval about t 0
コメント
コメントを投稿